Rail careers attract those who enjoy hands-on work and seeing results. A railroad worker keeps transport moving, handling operations, safety, and teamwork that connect communities.
Training and job opportunities range from operating locomotives to maintaining signal systems. Each role provides distinct challenges, rewards, and growth potential for those ready to learn.
This guide by Insiderbits shares practical insights, career paths, and benefits in the rail sector. Keep reading to see how these opportunities could match your ambitions perfectly.
Related: Auto Mechanic Courses Online: Study Car Repair at Home
What does a railroad worker do today?
Modern rail operations blend tradition with advanced technology, requiring professionals to operate trains, maintain tracks, and make sure safety systems run without interruption.
Roles span from equipment inspection to coordination in control centers, linking every stage of the journey. These tasks demand precision and commitment from every railroad worker.
With rail lines connecting cities and industries, daily duties influence economic flow and public mobility, making these professionals essential to both community life and national infrastructure.
From steel tracks to digital control: how the job evolved
Early rail work focused on manual track laying and mechanical train operation. Now, GPS, automated braking, and remote monitoring define a highly technical environment.
Specialized software, sensor networks, and advanced materials allow faster travel and safer operations, transforming the profession into one that blends hands-on skills with expertise.
Daily tasks you might not expect
Some responsibilities extend beyond operating locomotives, involving diverse and surprising contributions to rail safety, efficiency, and passenger comfort.
- Coordinating weather response: adjusting schedules and maintenance during storms to minimize disruption and protect rail integrity;
- Monitoring wildlife impact: preventing and managing animal encounters along tracks to safeguard passengers and the environment;
- Testing track geometry: using specialized equipment to detect minute deviations that could affect speed or safety;
- Adapting to seasonal shifts: preparing rail systems for temperature extremes, ensuring consistent performance year-round.
Teamwork and safety as the backbone of operations
Collaboration unites engineers, conductors, and maintenance crews in complex tasks where precision and timing are critical for safety and efficiency as a railroad worker.
Regular safety drills, shared protocols, and real-time communication systems keep every member aligned, reducing risks and strengthening operational reliability across all rail networks.
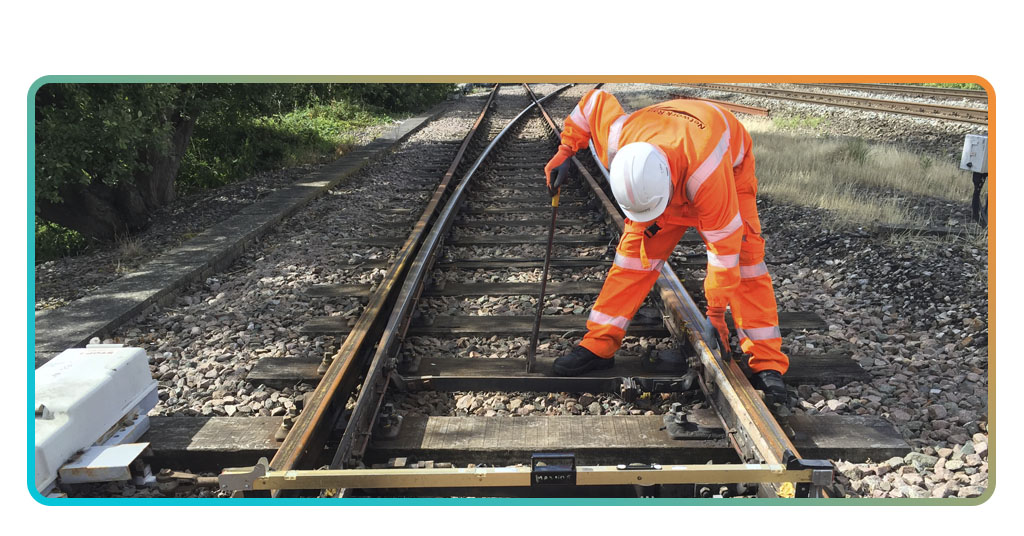

How to get started: courses and certifications
Learning the skills for a rail career starts with specialized training focused on safety, operations, and technical knowledge. Courses range from basic instruction to advanced programs.
Certification ensures compliance with national standards and improves employability. Many programs combine classroom learning with practical exercises.
RailPros online training
| Pricing: | Paid, and prices vary from $200 and up. |
| Available For: | Web. |
RailPros Online Training provides practical courses that prepare learners for rail industry demands, offering technical knowledge and confidence to begin working as a railroad worker.
Courses cover rail safety, equipment handling, track inspection, and operational rules, presented in a clear structure suitable for beginners and experienced rail professionals.
Interactive lessons and real-world examples connect theory to practical tasks, helping learners build skills while meeting industry standards and current regulatory requirements.
RailPros’ best features
- Comprehensive course library: offers safety, technical, and operational modules that prepare learners for multiple rail industry roles with practical, up-to-date content;
- Industry-recognized certifications: credentials meet national standards, boosting career opportunities and professional credibility for those aiming to succeed in the field;
- Practical learning approach: combines interactive lessons with real-life case studies, ensuring concepts are immediately applicable in modern rail work environments.
NARS training center
| Pricing: | Paid, but prices are not publicly available. |
| Available For: | Web. |
The NARS Training Center provides hands-on programs that build practical rail skills, helping individuals move toward employment as a qualified railroad worker.
Its curriculum includes safety procedures, track maintenance, signaling systems, and operational rules, offering structured learning suitable for both beginners and rail professionals.
Modern facilities and experienced instructors ensure students gain real-world insights, preparing them to meet industry standards and perform effectively in various rail-related positions.
NARS’ best features
- Specialized industry programs: focused courses in safety, operations, and maintenance prepare learners for immediate application in rail careers;
- Hands-on training environment: realistic exercises develop technical expertise and confidence essential for achieving success as a professional in the field;
- Expert-led instruction: experienced rail professionals deliver lessons that connect classroom knowledge with real operational challenges and current industry standards.
Federal Railroad Administration
| Pricing: | Free training resources available, but it doesn’t directly offer free certification courses. |
| Available For: | Web. |
The Federal Railroad Administration sets national safety standards, certifies training programs, and supports individuals aiming to start a secure career as a railroad worker.
Its regulations cover track safety, equipment standards, operational procedures, and emergency protocols, ensuring consistent quality and compliance across all aspects of the rail industry.
Through grants, research, and oversight, the agency promotes innovation, enhances safety, and strengthens the long-term stability of rail operations throughout the country.
Federal Railroad Administration’s best features
- Safety standards: establishes strict rules for track maintenance, equipment operation, and worker training to ensure consistent safety across all rail networks;
- Certified training oversight: approves programs meeting federal requirements, improving job readiness for individuals seeking employment as qualified professionals;
- Research support: funds studies and projects that improve rail technology, operational efficiency, and long-term sustainability for the transportation industry nationwide.
Related: Get certified for technician jobs with free online courses
Job options: from conductor to signal technician
Rail careers cover a wide range of responsibilities, from managing passenger service schedules to maintaining intricate signaling and communication systems across vast networks.
Each role demands specific abilities, offering pathways for those starting fresh and for professionals seeking advancement as a skilled railroad worker.
Entry-level roles you can land without a diploma
Many rail positions focus on practical skills, allowing motivated learners to begin work and get on-the-job training without any formal academic qualifications.
- Train conductor assistant: supports conductors with passenger coordination, schedule updates, and ticket verification during active service hours;
- Track laborer: performs inspections, repairs, and seasonal maintenance on rail infrastructure to ensure safe train passage in all conditions;
- Rail yard worker: organizes railcars, manages equipment, and ensures smooth daily yard operations supporting freight and passenger services;
- Signal maintenance helper: assists in inspecting and repairing signal systems, learning technical processes while ensuring network reliability and safety.
Skilled technical paths for experienced workers
A railroad worker in a technical role needs specialized knowledge learned through vocational programs, certifications, or years of hands-on experience with operational procedures.
Signal technicians install, maintain, and upgrade systems that control train movements, while electricians manage the vital power infrastructure, ensuring safe and efficient rail operations.
Mechanical specialists service and repair locomotives and rolling stock, using advanced tools to maintain efficiency, safety, and performance standards, keeping trains reliable for transportation.
Growth opportunities in maintenance, engineering, and safety
Specialized maintenance teams handle everything from track welding to high-tech diagnostics, making them critical to smooth daily operations for every railroad worker.
Engineering positions involve designing rail improvements, overseeing construction, and ensuring projects meet operational, safety, and environmental requirements across locations.
Safety management professionals monitor compliance, train staff in emergency protocols, and develop strategies to prevent accidents while improving long-term operational resilience.

Must-have skills and education requirements
Rail careers require a mix of physical, technical, and interpersonal abilities, along with formal or vocational training suited to industry standards.
Some positions demand certifications or licenses, while others offer on-the-job learning opportunities that still require a foundation of essential knowledge as a railroad worker.
Education levels vary by role, but every position benefits from continuous learning to stay aligned with safety regulations and technological advancements in the rail sector.
Physical abilities and safety awareness
Rail work often involves long hours, variable weather conditions, and physically demanding tasks that require strength, stamina, and attention to safety procedures.
Consistent adherence to safety rules protects workers and passengers while ensuring rail systems operate without unnecessary delays or preventable incidents.
Technical know-how for modern rail systems
Modern rail relies on advanced signaling, automated controls, and specialized equipment, making technical competence essential for efficiency and operational reliability.
Knowledge in electrical systems, mechanical maintenance, and digital monitoring tools enables workers to troubleshoot and keep operations running smoothly under demanding conditions.
Soft skills: communication, problem-solving, and adaptability
Clear communication ensures coordination between teams, especially in time-sensitive situations where precise instructions can prevent delays or safety risks for a railroad worker.
Problem-solving and adaptability allow workers to respond effectively to unexpected challenges, adjusting plans quickly while maintaining operational goals and safety standards.
Related: Carpentry Courses Online: Learn Woodworking Step by Step
Salaries, unions, and benefits by state
Rail compensation can vary widely, with some states offering higher wages, stronger union protections, and more comprehensive benefits packages for workers in different roles.
Collective bargaining often secures better healthcare, retirement options, and job stability, strengthening the long-term outlook for any committed and skilled railroad worker.
Amtrak careers
Amtrak offers positions in passenger operations, maintenance, engineering, and corporate services, each with competitive pay and benefits tailored to the role’s demands.
Employees may access comprehensive healthcare, retirement savings programs, and paid leave, alongside opportunities for advancement in diverse areas of the company.
Training programs focus on safety, customer service, and technical skills, ensuring staff meet operational standards while developing professionally over the long term.
Union Pacific careers
Union Pacific offers opportunities in freight operations, maintenance, and logistics, providing stability, competitive pay, and benefits that help retain a skilled and dedicated railroad worker.
Workers get specialized training and certifications, improving both safety and efficiency across the company’s expansive and strategically important rail network.
Employee programs include tuition assistance, health insurance, and wellness initiatives, showing a strong commitment to long-term workforce satisfaction and professional retention.
Average pay ranges across the U.S.
Pay rates vary by region, role, and experience, with some states offering premiums for specialized skills or particularly challenging work conditions in the industry.
High-demand areas may provide additional incentives, such as housing allowances or relocation support, to attract qualified professionals into essential rail industry positions.
Understanding pay trends helps individuals assess opportunities, negotiate effectively, and choose career paths aligning with their financial goals and preferred work environments.
Union support: how it strengthens your career
Strong unions negotiate better wages, protect employee rights, and ensure safe working environments, making them a vital part of a rewarding career for a railroad worker.
Membership includes access to legal support, training resources, and collective bargaining advantages. These benefits contribute to long-term job satisfaction and workplace stability.
Unions also play a key role in resolving disputes, securing improved benefits, and keeping communication open between employees and management, fostering a positive environment.

Your rail career starts with solid training
Building a career in rail offers stability, growth, and valuable skills, with opportunities available in operations, maintenance, engineering, and safety across many states nationwide.
Created with care by Insiderbits, this guide connects essential details, training options, and career insights for anyone aiming to succeed as a professional railroad worker.
Keep reading Insiderbits for more articles featuring practical advice, industry overviews, and detailed resources designed to support informed decisions in your professional path.