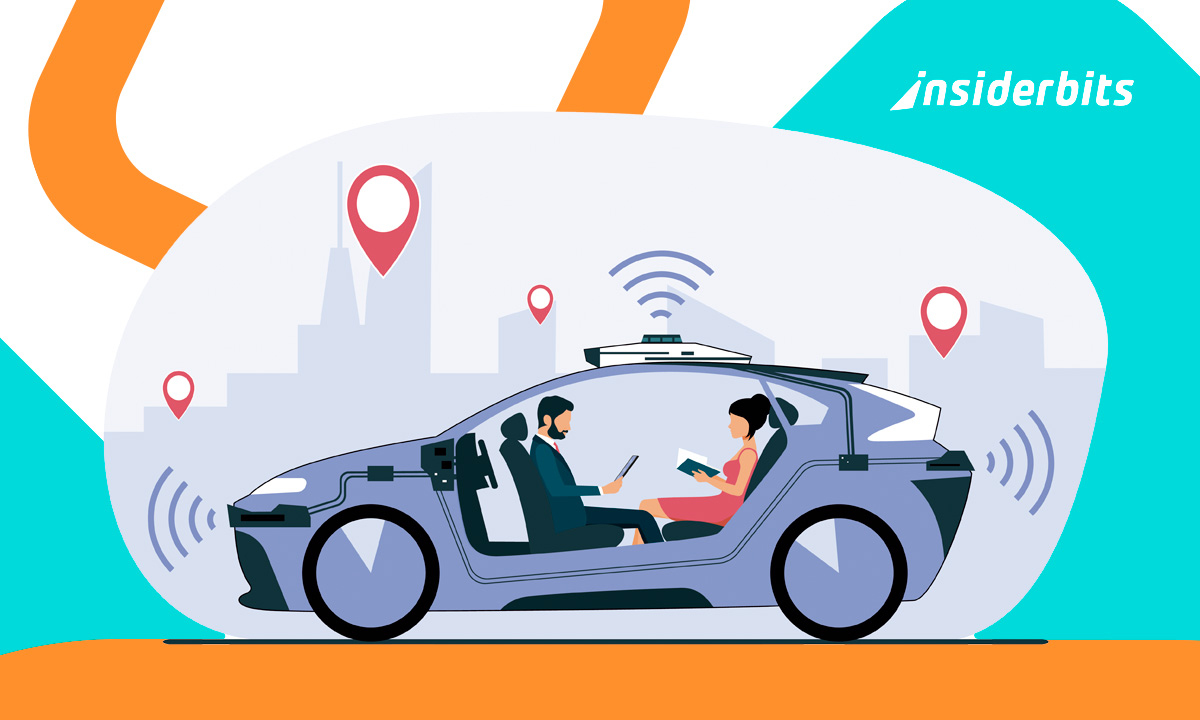
The rise of self-driving transport marks a turning point in how cities manage mobility, offering a glimpse into a future shaped by automation and efficiency. It has started to appear in real operations autonomous buses and trains across the globe, slowly redefining urban transit.
While technical and ethical challenges remain, the movement toward a driverless model is steadily gaining public and governmental attention. The big question is when and which cities and technologies will lead that transition successfully.
- Beste Fahrspiele: Holen Sie sich hinter dem Lenkrad der Spaß
- Canada Driving Test: Your Ultimate Guide to Passing the Exam
- Conquer the Streets in Driving Real Race City 3D
The Future of Self-Driving Public Transport: Are We There Yet?
The deployment of self-driving transport in public systems has already begun, with autonomous shuttle routes and automated trains piloted in select cities.
Though most of these services operate in limited settings, such as airports or university campuses, they demonstrate that the infrastructure and software are maturing fast.
In addition, places like Geneva, Seoul, and some parts of the U.S., pilot programs are transitioning into long-term strategies for integrating autonomous mobility into broader transit networks.
Not all cities, however, advance at the same pace due to funding gaps or regulatory friction surrounding AI-driven safety.
Some regions prioritize experimentation and legislative reform, while others remain cautious, waiting for stronger proof of success before scaling up.
The widespread adoption of driverless public systems will require synchronized investment, legal frameworks, and trust-building through public education.
How Autonomous Buses and Trains Work
Autonomous public vehicles rely on a combination of LiDAR sensors, cameras, radar systems, and machine learning algorithms to navigate streets and adapt to real-time data.
These systems process massive volumes of environmental input to make split-second decisions that simulate human reflexes with machine consistency.
Moreover, redundant systems ensure safety, while GPS and centralized traffic control integration allow autonomous units to sync with citywide traffic and rail systems.
This technological ecosystem transforms complexity into coordinated operations, allowing vehicles to function efficiently in dense environments.
In the case of autonomous trains, real-time data governs not only navigation but also passenger flow optimization.
By relying on software precision and predictive modeling, these systems achieve a level of consistency that enhances safety and operational efficiency.
Safety Concerns: Can Self-Driving Transport Be Trusted?
Safety remains the defining issue in the discussion around self-driving transport, as public trust hinges on a system’s ability to avoid harm in unpredictable scenarios.
Despite hundreds of successful test runs, a few high-profile incidents have shaped perception, reinforcing concerns about software glitches, which can lead to decision-making limits.
Therefore, some critics argue that machine logic lacks the moral flexibility humans apply in high-stakes moments, while proponents highlight that most collisions are still human-caused.
In many cases, public opinion is driven more by isolated stories than by consistent safety records, which challenges efforts to build long-term acceptance.
To counteract that perception, developers and transit agencies must emphasize transparency, invest in rigorous testing, and implement visible safety measures.
As long as skepticism persists, communication will be as important as performance in convincing the public that autonomy can equal, or even surpass, human reliability.
Cities Leading the Way in Autonomous Public Transport
Several cities have positioned themselves at the forefront of self-driving transport, adopting autonomous mobility not as an experiment but as part of long-term transit reform.
As Insiderbits pointed out above, there’s already cities in Asia and Europe that already count with this service. Meanwhile, in America, some states still deal with legal frameworks.
In many cases, smaller routes like last-mile connections or feeder lines serve as proving grounds for broader implementation in dense metro areas.
These gradual implementations allow cities to study public response and build operational expertise before expanding into more complex routes.
Consequently, support from local governments and policy flexibility play a decisive role in determining which cities advance more quickly than others in adopting autonomous systems.
The cities taking these early steps are also redefining how urban transit planning is envisioned for the next decade.
The Pros and Cons of a Driverless Future
The promise of self-driving transport includes reduced traffic accidents, lower emissions, and improved transit efficiency, particularly in underserved or low-density areas.
Without human error or fatigue, driverless systems could optimize routes and cut operational costs for city governments and private operators.
However, this shift also raises concerns about job displacement, system vulnerabilities, and reliance on AI for critical public functions.
Every benefit comes with a set of trade-offs that must be addressed thoughtfully through public engagement.
Maximizing the advantages of automation requires clear investment in cybersecurity protocols and inclusive infrastructure planning.
The success of this transition will depend not just on engineering, but on a shared vision between technologists and public officials.
Self-Driving Public Transport: When Will It Become the Norm? – Conclusion
The evolution of self-driving transport represents a redefinition of public mobility. As cities experiment with autonomous systems, the continued investment in autonomous technology reveals a global momentum that’s difficult to ignore.
Widespread adoption will not occur overnight, but as successful examples accumulate and systems mature, more cities will treat autonomy as a necessity.
The future of public transport will not be defined solely by the absence of drivers, but by the ability of these systems to serve diverse populations with greater reliability, inclusivity, and environmental responsibility.
Related: Brave: Eco-Driving-Technologie: Apps für kraftstoffsparende Routenplanung
Hat Ihnen dieser Artikel gefallen? Speichern Sie den Insiderbits-Blog unter Ihren Favoriten, um die neuesten Tools, kreativen technischen Tipps und bahnbrechenden Entwicklungen in der Bildbearbeitung zu erhalten!